No último dia 27/04 o Prof. Carlos Bueno esteve em Salvador, onde ministrou aula para os alunos doNEAB- Núcleo Avançado de Endodontia da Bahia, coordenado pelo prof. Alexandre Villela eauxiliado pelo Prof Marcos Rios (aluno do curso de mestrado de excelência em Endodontia da EEC) . Os assuntos ministrados foram Retratamento Endodôntico: previsibilidade e técnicas. e ainda Microinfiltração em Endodontua: selamento pós-endodontia e uso dos pinos de fibra.
segunda-feira, 29 de abril de 2013
quinta-feira, 25 de abril de 2013
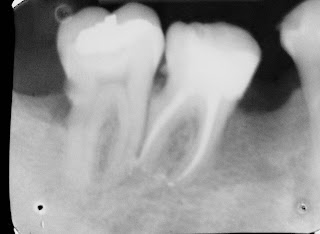
Caso Clínico Interessante do Prof. Carlos E. da Silveira Bueno - Tratamento Endodôntico com Sistema Reciprocante / PathFiles / 4o Canal
O caso a seguir nos mostra a importância do conhecimento da anatomia de molares superiores.
O tratamento Endodôntico do dente 17 foi realizado em uma única sessão com
auxílio de instrumento Reciprocante Wave One e Pathfiles. Porém ao final da obturação
dos canais Vestibulares (MV e DV) e Palatino observou-se um ponto mais próximo ao canal Palatino (incomum nesses casos) que denotou ser o 4o canal deste elemento. Dessa forma sua instrumentação e obturação foi realizada em sequência.
Utilização de Limas PathFiles
Instrumentação Reciprocante - WaveOne
Irrigação com Sol. de Hipoclorito de Sódio 2,5% e ao final EDTA 17%
Ambas ativadas com PUI - Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation
PUI - (3 ciclos de 10s por canal/por solução - Hipoclorito/EDTA/Hipoclorito)
Obturação com Onda Contínua de Condensação + Cimento Ah-Plus
Selamento coronário pós-endodontia realizado com Cimpat e Resina Composta.
quarta-feira, 24 de abril de 2013
terça-feira, 23 de abril de 2013
segunda-feira, 22 de abril de 2013
Caso Clínico da Aluna de Mestrado de Excelência em Endodontia da EEC - Paula Regina de Oliveira
Paciente de 85 anos de idade, encaminhada para retratamento da UD 15. Após anamenese, exame clínico e radiográfico evidenciou-se que o problema encontrava-se na UD 16. Notar o elevado grau de calcificação da câmara pulpar e atresia dos canais radiculares, sendo necessárias 3 sessões para localização e tratamento de todos os canais.
Aluno do Mestrado em Excelência em Endodontia da EEC no AAE 2013 Hawai - Marcelo Coelho
O aluno do curso de Mestrado de Excelência em Endodontia da Equipe de Endodontia de Campinas , Marcelo Coelho, esteve na última semana no Hawaí durante o Congresso da AAE - Association of American Endodontic para uma apresentação de trabalho científico (Oral Research Presenter) durante o evento.
Int Endod J april 2013 - Efficacy of lasers as an adjunct to chemo-mechanical disinfection of infected root canals: a systematic review
Efficacy of lasers as an adjunct to
chemo-mechanical disinfection of infected
root canals: a systematic review
H. Fransson1*, K. M. Larsson2 & E. Wolf1
1Department of Endodontics, Faculty of Odontology, Malmo ̈ University, Malmo ̈; and 2Department of Pedodontics, Faculty of
Odontology, Malmo ̈ University, Malmo ̈, Sweden
Abstract
The aim was to evaluate the efficacy of various types
of lasers used as an adjunct to chemo-mechanical dis-
infection of infected root canals with the outcome
measures ‘normal periapical condition’ or ‘reduction
of microbial load’. PubMed, CENTRAL and ISI Web of
Knowledge literature searches with specific indexing
terms and a subsequent hand search were made with
stated limits and criteria. Relevant publications were
retrieved, followed by interpretation. The quality of
each included publication was assessed as high, mod-
erate or low. The initial search process yielded 234
publications. All abstracts of these publications were
read, and the reference lists of relevant publications
were hand-searched. Ten articles were read in full text and interpreted according to a data extraction
form. Five were included in the systematic review and
were assessed. A meta-analysis was impossible to per-
form because the included studies were heterogeneous
with regard to study design, treatment and outcome
measures. Positive effects were reported; however, no
concluding evidence grade could be made because
each included study was judged to have low quality,
primarily due to lack of a power analysis, blinding
and reproducibility. The evidence grade for whether
lasers can be recommended as an adjunct to chemo-
mechanical disinfection of infected root canals was
insufficient. This does not necessarily imply that laser
should not be used as an adjunct to root canal treat-
ment but instead underscores the need for future
high-quality studies.
Keywords: chemo-mechanical, disinfection, endodon-
tics, infection, lasers, systematic review.
download paper in pdf
domingo, 21 de abril de 2013
quinta-feira, 18 de abril de 2013
JOE april 2013 - In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of a Novel Root Repair Material
In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of a Novel Root
Repair Material
Hui-min Zhou, PhD,*† Ya Shen, DDS, PhD,† Zhe-jun Wang, DDS, PhD,†‡ Li Li, PhD,* Yu-feng Zheng, PhD,*§ Lari Ha€kkinen, DDS, PhD,jj and Markus Haapasalo, DDS, PhD†
Download paper in pdf
Repair Material
Hui-min Zhou, PhD,*† Ya Shen, DDS, PhD,† Zhe-jun Wang, DDS, PhD,†‡ Li Li, PhD,* Yu-feng Zheng, PhD,*§ Lari Ha€kkinen, DDS, PhD,jj and Markus Haapasalo, DDS, PhD†
Abstract
Introduction: This study examined the effect of a new bioactive dentin substitute material (Biodentine) on the viability of human gingival fibroblasts.
Methods: Bio- dentine, White ProRoot mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), and glass ionomer cement were evaluated. Human gingival fibroblasts were incubated for 1, 3, and 7 days both in the extracts from immersion of set materials in culture medium and directly on the surface of the set materials immersed in culture medium. Fibro- blasts cultured in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium were used as a control group. Cytotoxicity was evaluated by flow cytometry, and the adhesion of human gingival fibroblasts to the surface of the set materials was as- sessed by using scanning electron microscopy. The data of cell cytotoxicity were analyzed statistically by using a one-way analysis of variance test at a signifi- cance level of P < .05.
Results: Cells exposed to extracts from Biodentine and MTA showed the highest viabilities at all extract concentrations, whereas cells exposed to glass ionomer cement extracts displayed the lowest viabilities (P < .05). There was no significant difference in cell viabilities between Biodentine and MTA during the entire experimental period (P > .05). Human gingival fibroblasts in contact with Biodentine and MTA attached to and spread over the material surface after an overnight culture and increased in numbers after 3 and 7 days of culture.
Conclusions: Biodentine caused gingival fibroblast reaction similar to that by MTA. Both materials were less cytotoxic than glass ionomer cement. (J Endod 2013;39:478–483)
Key Words
Biocompatibility, Biodentine, calcium silicate–based
materials, cell adhesion, cytotoxicity, flow cytometry,
glass ionomer, human gingival fibroblast, MTAIntroduction: This study examined the effect of a new bioactive dentin substitute material (Biodentine) on the viability of human gingival fibroblasts.
Methods: Bio- dentine, White ProRoot mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), and glass ionomer cement were evaluated. Human gingival fibroblasts were incubated for 1, 3, and 7 days both in the extracts from immersion of set materials in culture medium and directly on the surface of the set materials immersed in culture medium. Fibro- blasts cultured in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium were used as a control group. Cytotoxicity was evaluated by flow cytometry, and the adhesion of human gingival fibroblasts to the surface of the set materials was as- sessed by using scanning electron microscopy. The data of cell cytotoxicity were analyzed statistically by using a one-way analysis of variance test at a signifi- cance level of P < .05.
Results: Cells exposed to extracts from Biodentine and MTA showed the highest viabilities at all extract concentrations, whereas cells exposed to glass ionomer cement extracts displayed the lowest viabilities (P < .05). There was no significant difference in cell viabilities between Biodentine and MTA during the entire experimental period (P > .05). Human gingival fibroblasts in contact with Biodentine and MTA attached to and spread over the material surface after an overnight culture and increased in numbers after 3 and 7 days of culture.
Conclusions: Biodentine caused gingival fibroblast reaction similar to that by MTA. Both materials were less cytotoxic than glass ionomer cement. (J Endod 2013;39:478–483)
Key Words
Download paper in pdf
terça-feira, 16 de abril de 2013
segunda-feira, 15 de abril de 2013
domingo, 14 de abril de 2013
sábado, 13 de abril de 2013
quarta-feira, 10 de abril de 2013
Int Endod J april 2013 - Chitosan: a new solution for removal of smear layer after root canal instrumentation
Aim: To evaluate, by scanning electron microscopy
(SEM), the efficacy of smear layer removal using
chitosan compared with different chelating agents,
and to quantify, by atomic absorption spectrophotom-
etry with flame (AASF), the concentration of calcium
ions in these solutions after irrigation.
Methodology The root canals of twenty-five canines were prepared using a crown-down technique and irrigated with 1% sodium hypochlorite. The teeth were randomly divided into groups (n = 5), according to the type of final irrigation: 15% EDTA, 0.2% chito- san, 10% citric acid, 1% acetic acid and control (with- out final irrigation). The total volume of each chelating solution was collected from the canals and analysed by AASF for quantification of calcium ions in the solutions. Then, the roots were split longitudi- nally and examined by SEM for evaluation of smear layer removal in the middle and apical thirds. Clean- ing scores were attributed and analysed statistically using the Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn tests. The AASF data were analysed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey– Kramer test. A significant level of a = 0.05 was adopted.
Results: 15% EDTA, 0.2% chitosan and 10% citric
acid had similar smear layer removal capacity with a
significant difference (P < 0.05) from 1% acetic acid
and the control group. There was no significant differ-
ence (P > 0.05) between the smear layer remaining
in the middle and apical thirds. The highest calcium
ion concentration was observed with 15% EDTA
(121.80 ± 5.13) and 0.2% chitosan (104.13 ±
19.23), with no significant difference. The lowest cal-
cium ion concentration was obtained with 1% acetic
acid (25.62 ± 7.68), whilst 10% citric acid
(70.38 ± 11.15) had intermediate results, differing
significantly from the other solutions (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: 15% EDTA, 0.2% chitosan and 10% citric acid effectively removed smear layer from the middle and apical thirds of the root canal. 15% EDTA and 0.2% chitosan were associated with the greatest effect on root dentine demineralization, followed by 10% citric acid and 1% acetic acid.
Conclusions: 15% EDTA, 0.2% chitosan and 10% citric acid effectively removed smear layer from the middle and apical thirds of the root canal. 15% EDTA and 0.2% chitosan were associated with the greatest effect on root dentine demineralization, followed by 10% citric acid and 1% acetic acid.
terça-feira, 9 de abril de 2013
sexta-feira, 5 de abril de 2013
terça-feira, 2 de abril de 2013
Assinar:
Comentários (Atom)